Plug and Play
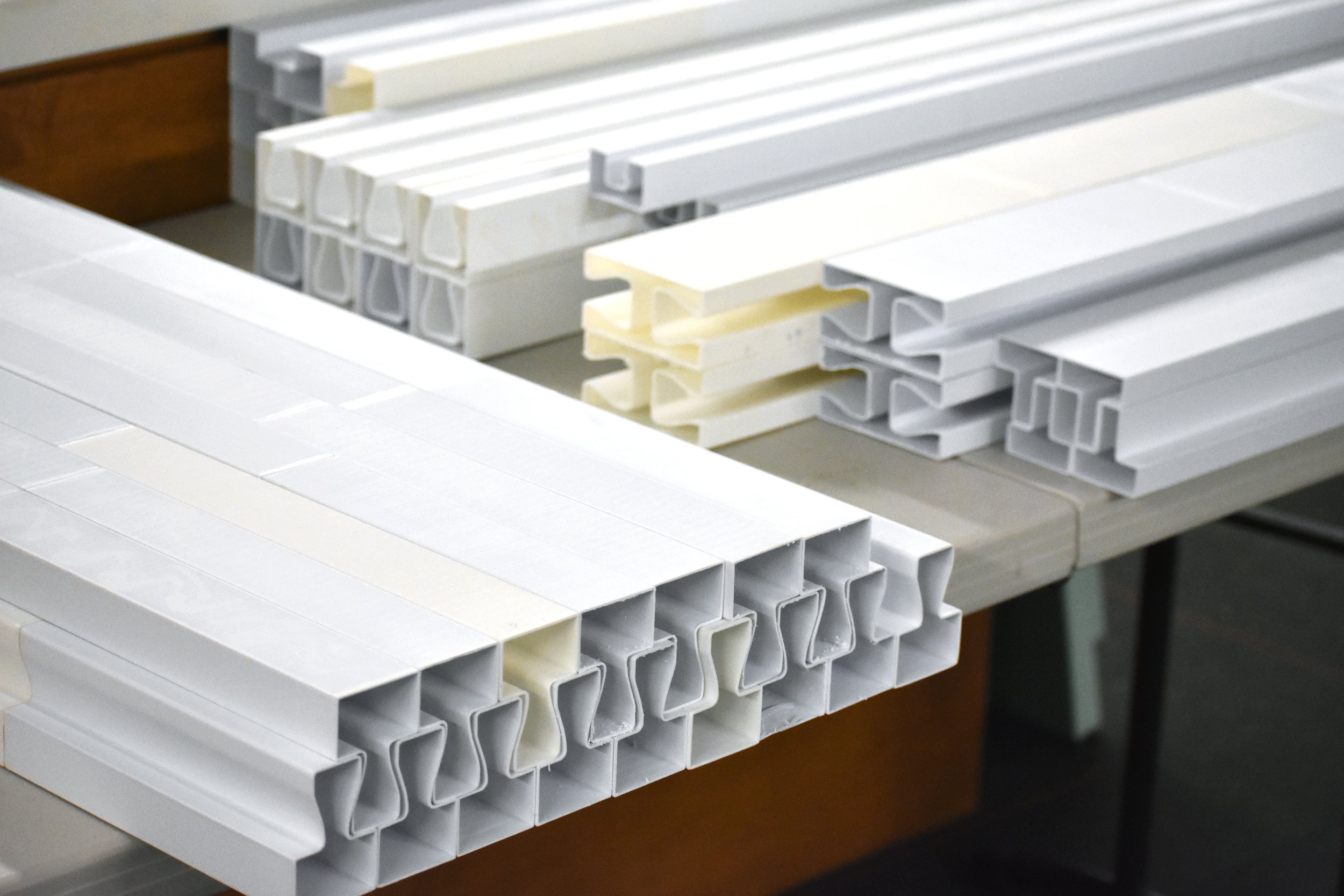
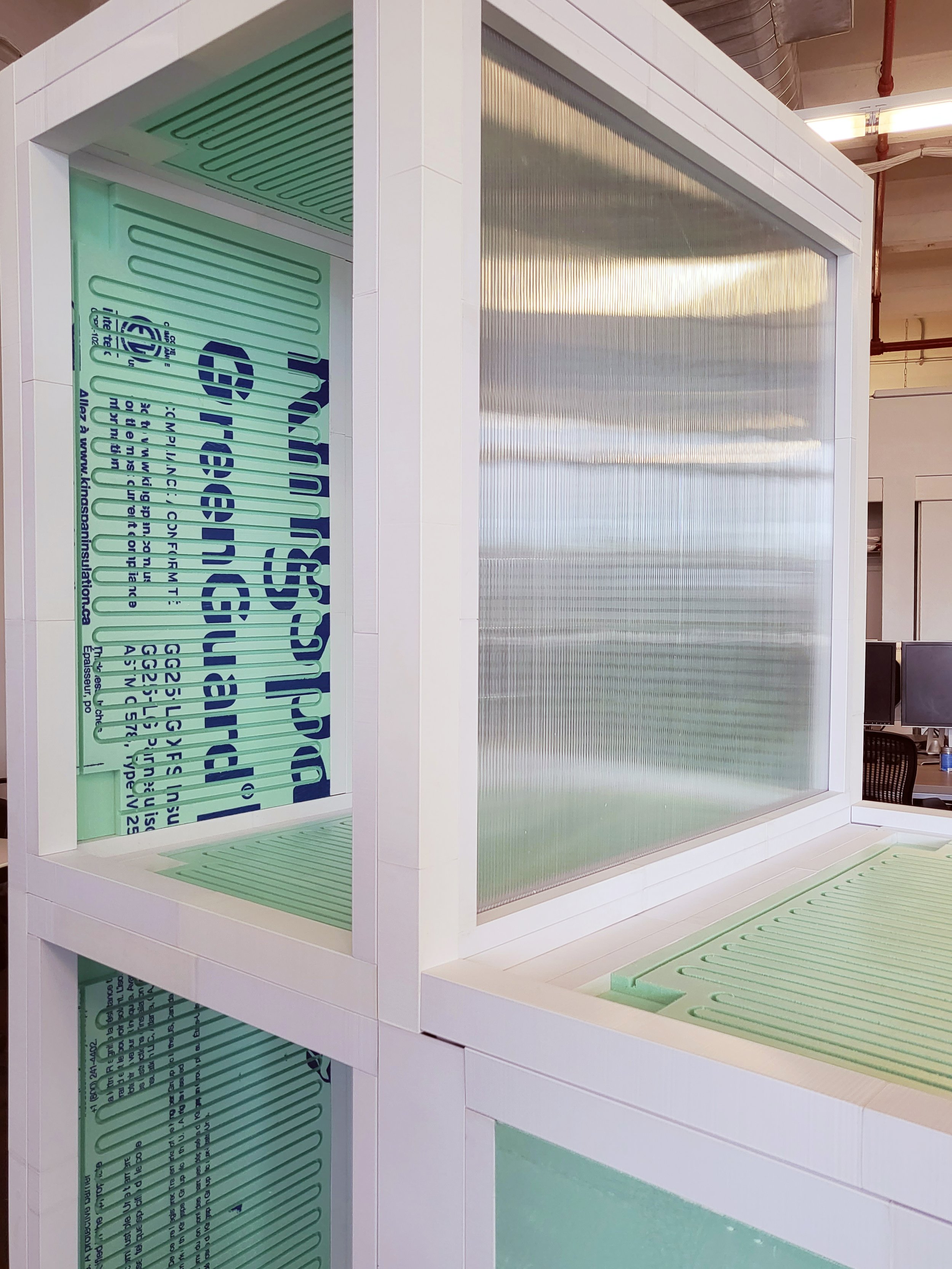
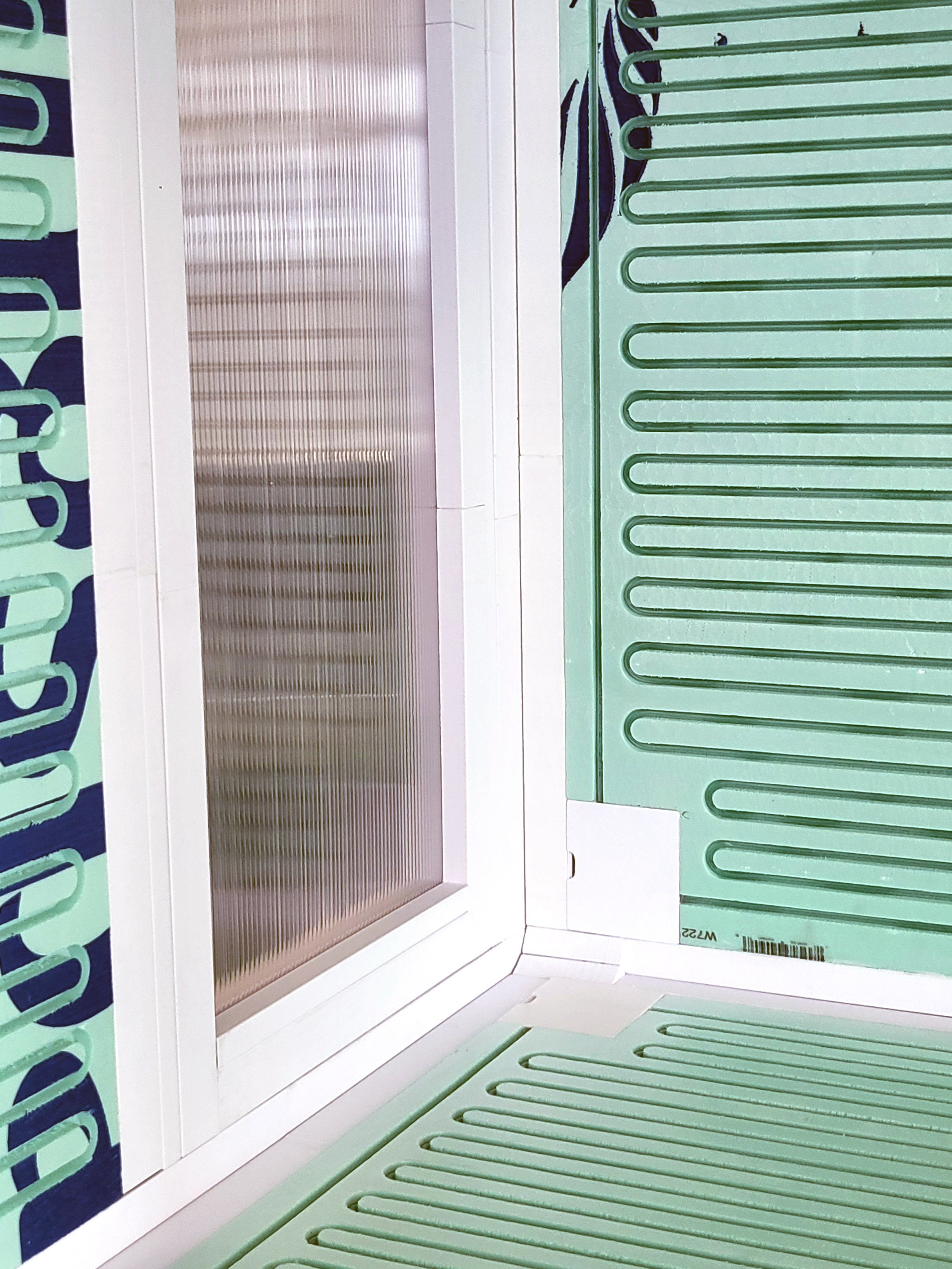
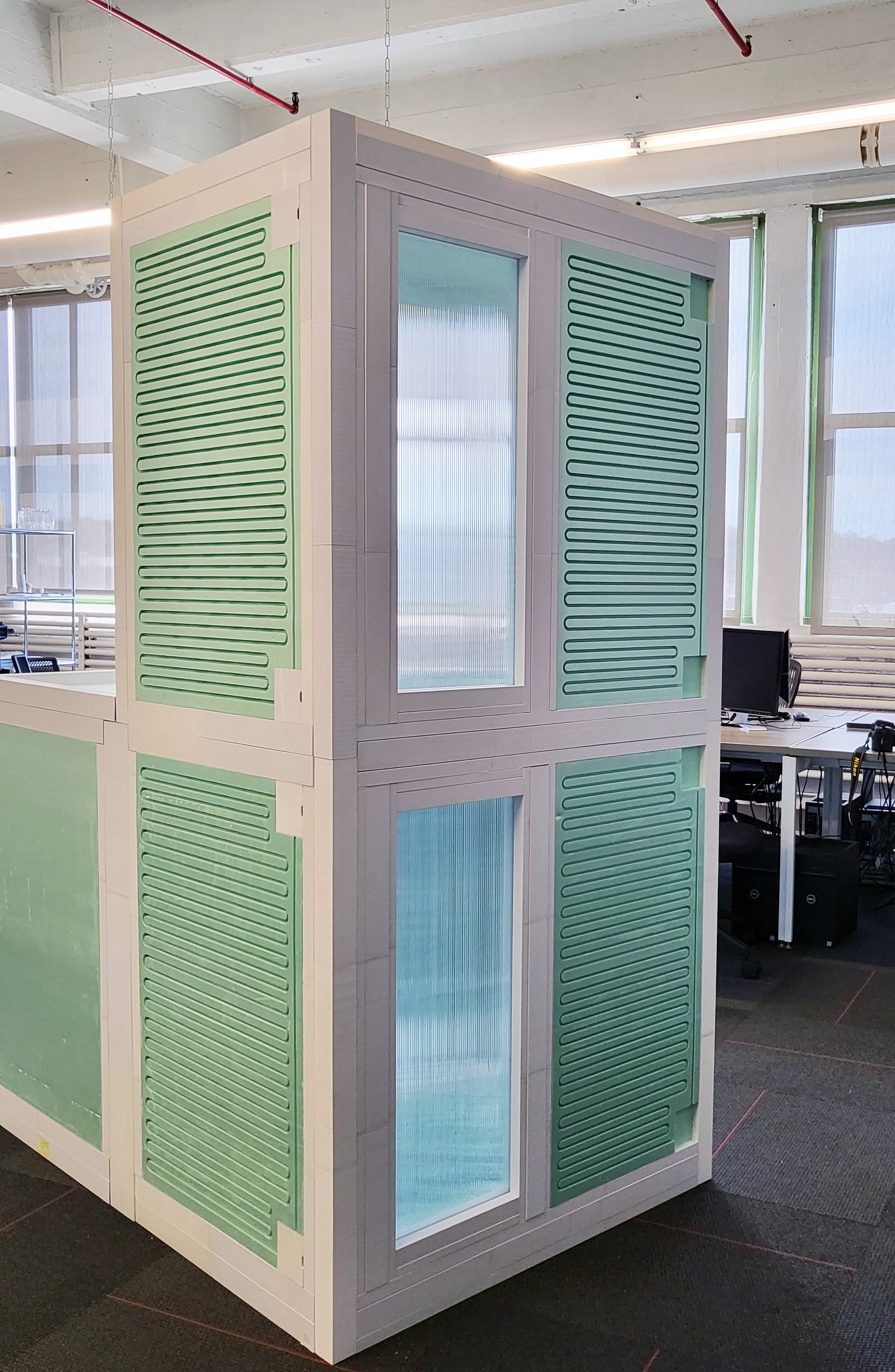




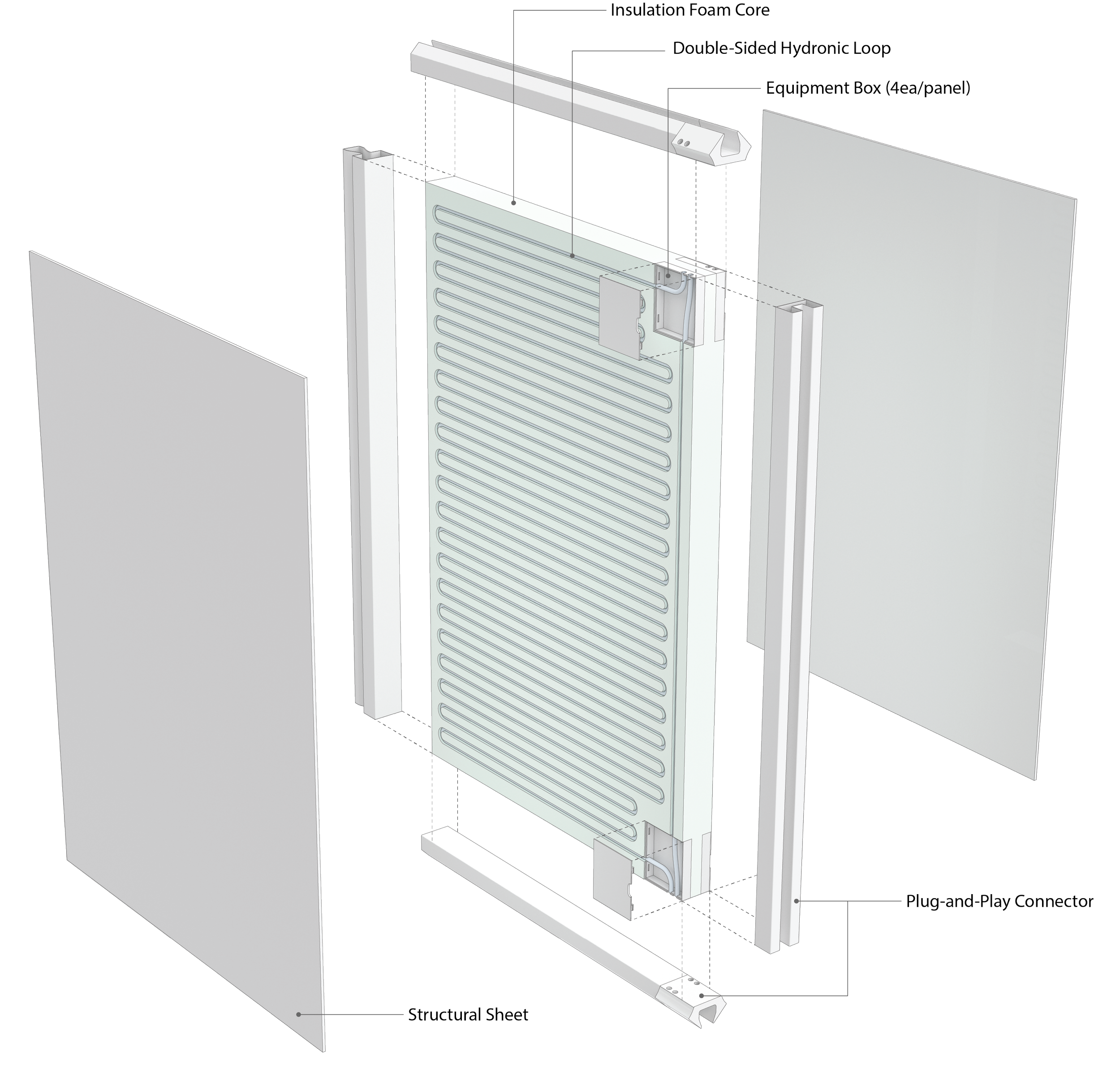

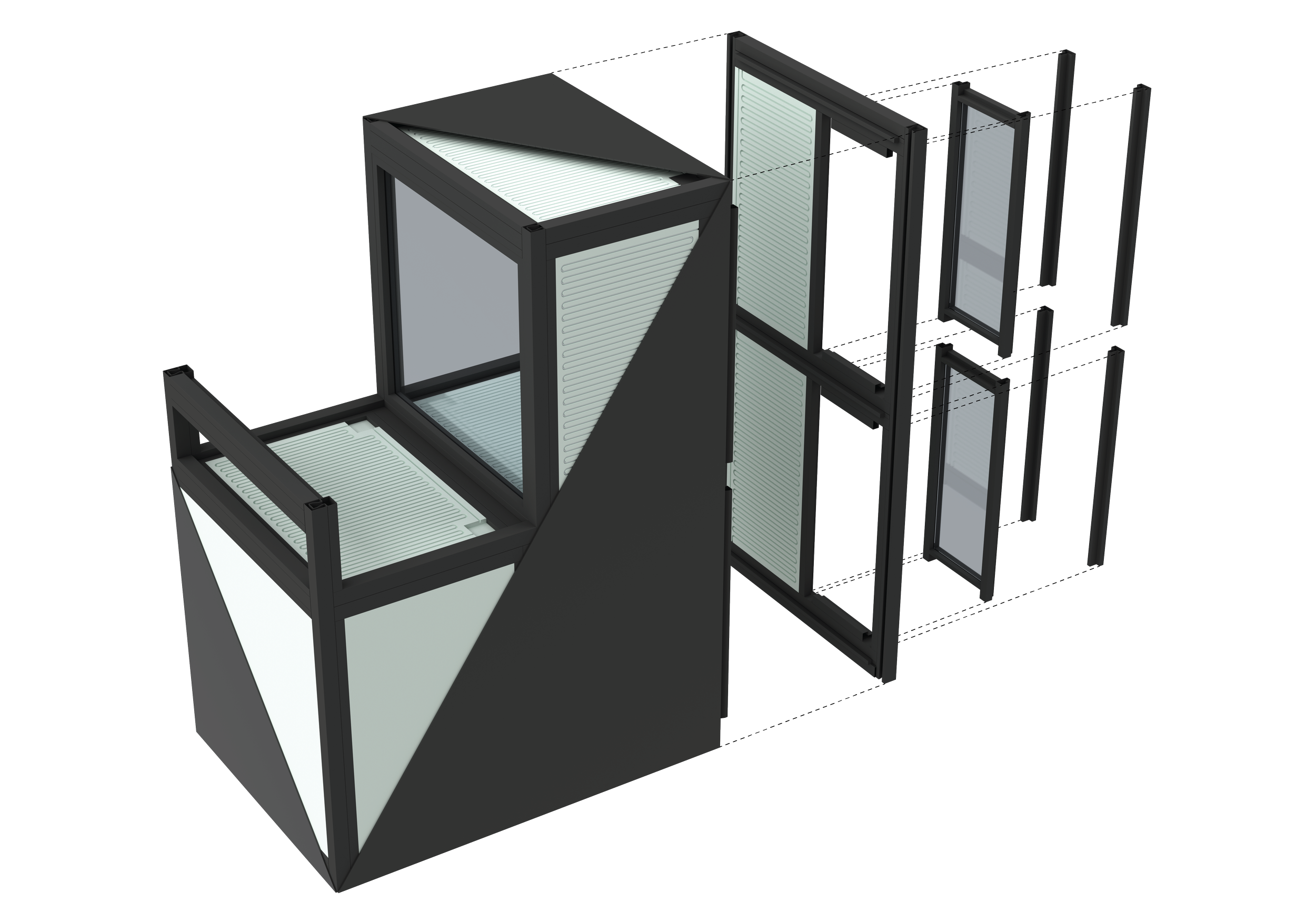

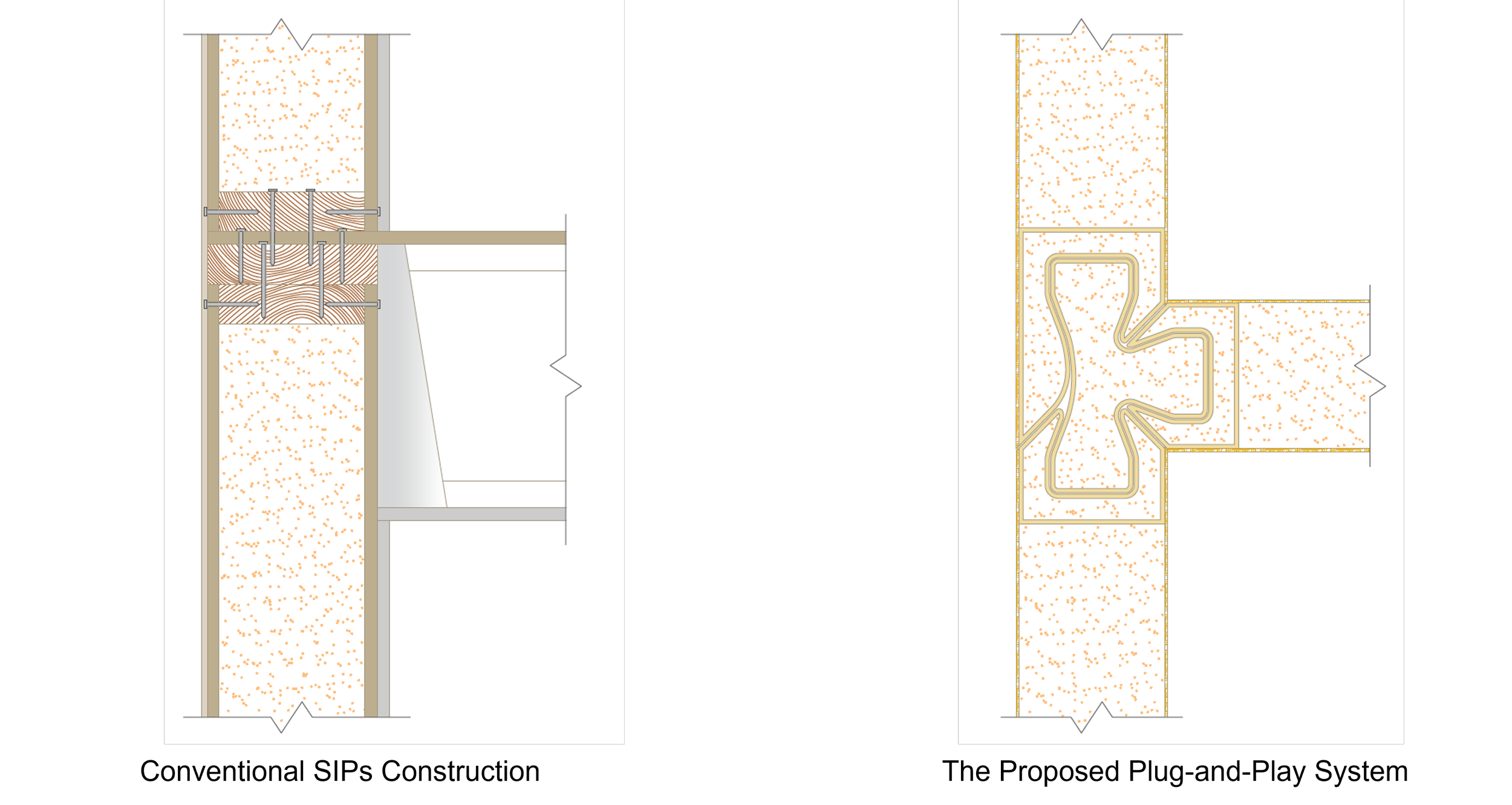
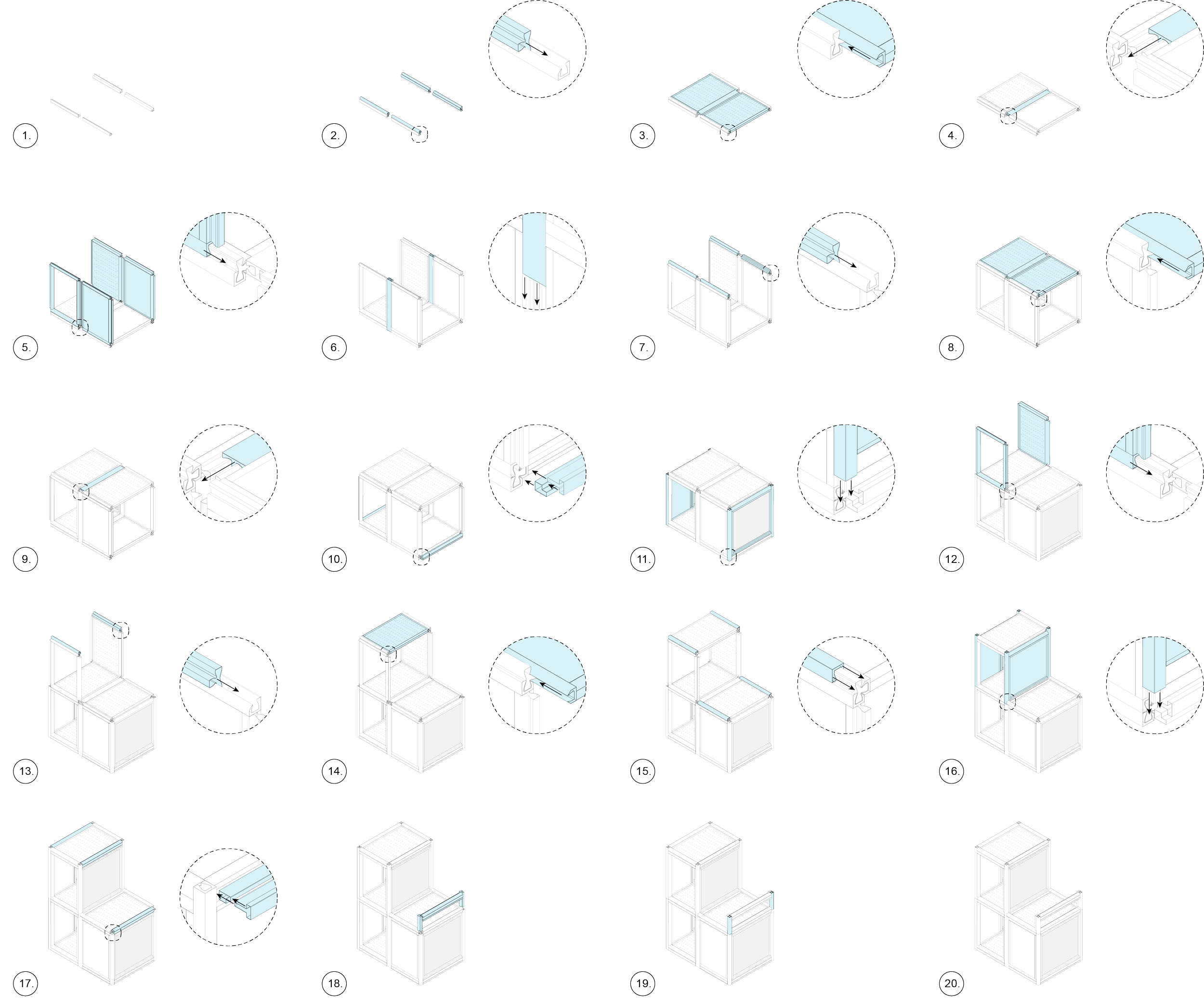
Modular building construction presents a viable approach to addressing the concern of global carbon emissions, of which 39% is attributed to building construction. In an effort to diminish this impact by reducing on-site labor demands and module fabrication processes, CASE is developing a flat packed, modular structural insulated panel (SIP) system. “Plug-and-Play”, enables the assembly of SIPs by sliding them both horizontally and vertically, securing the assembly in place.
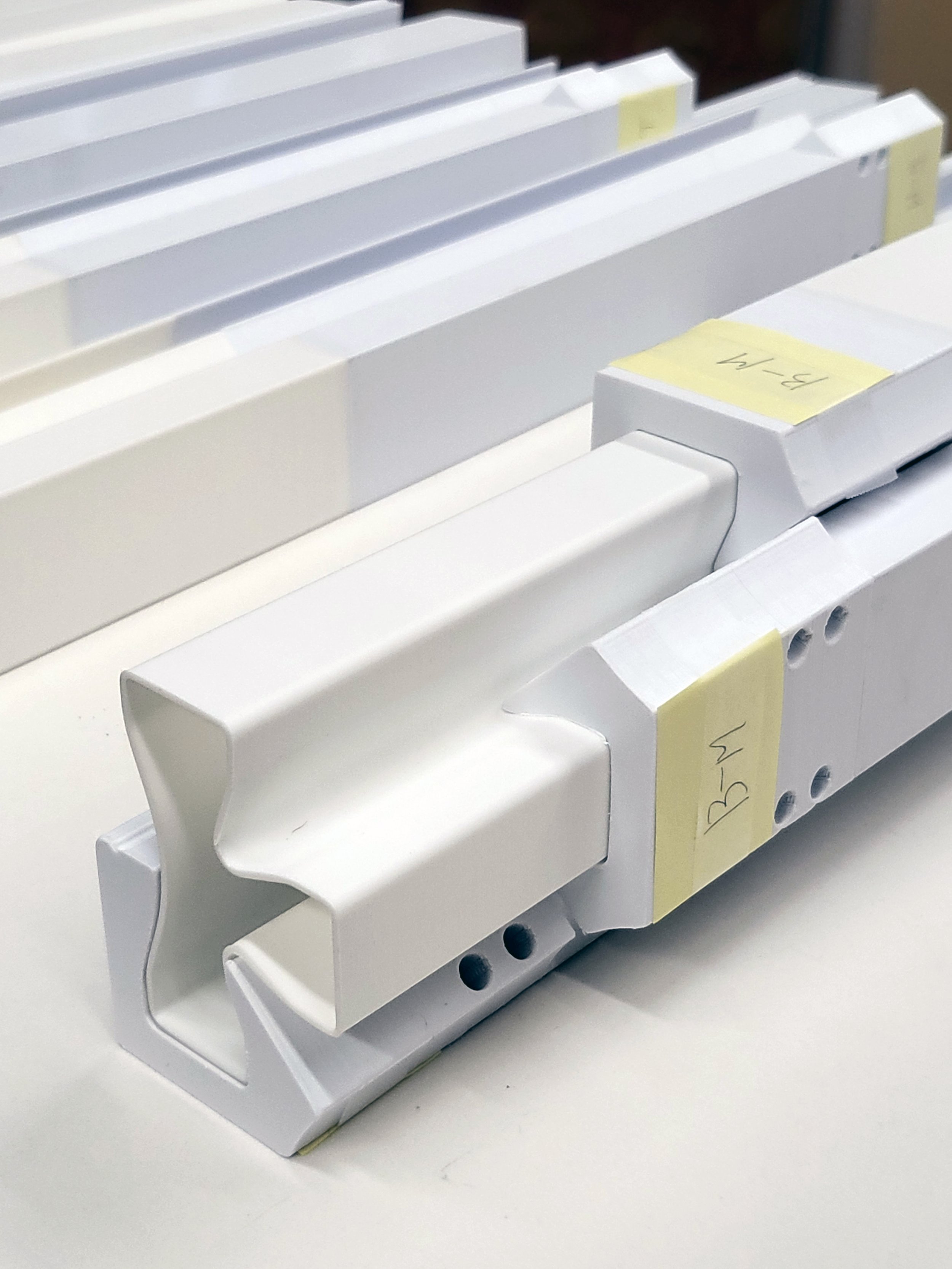
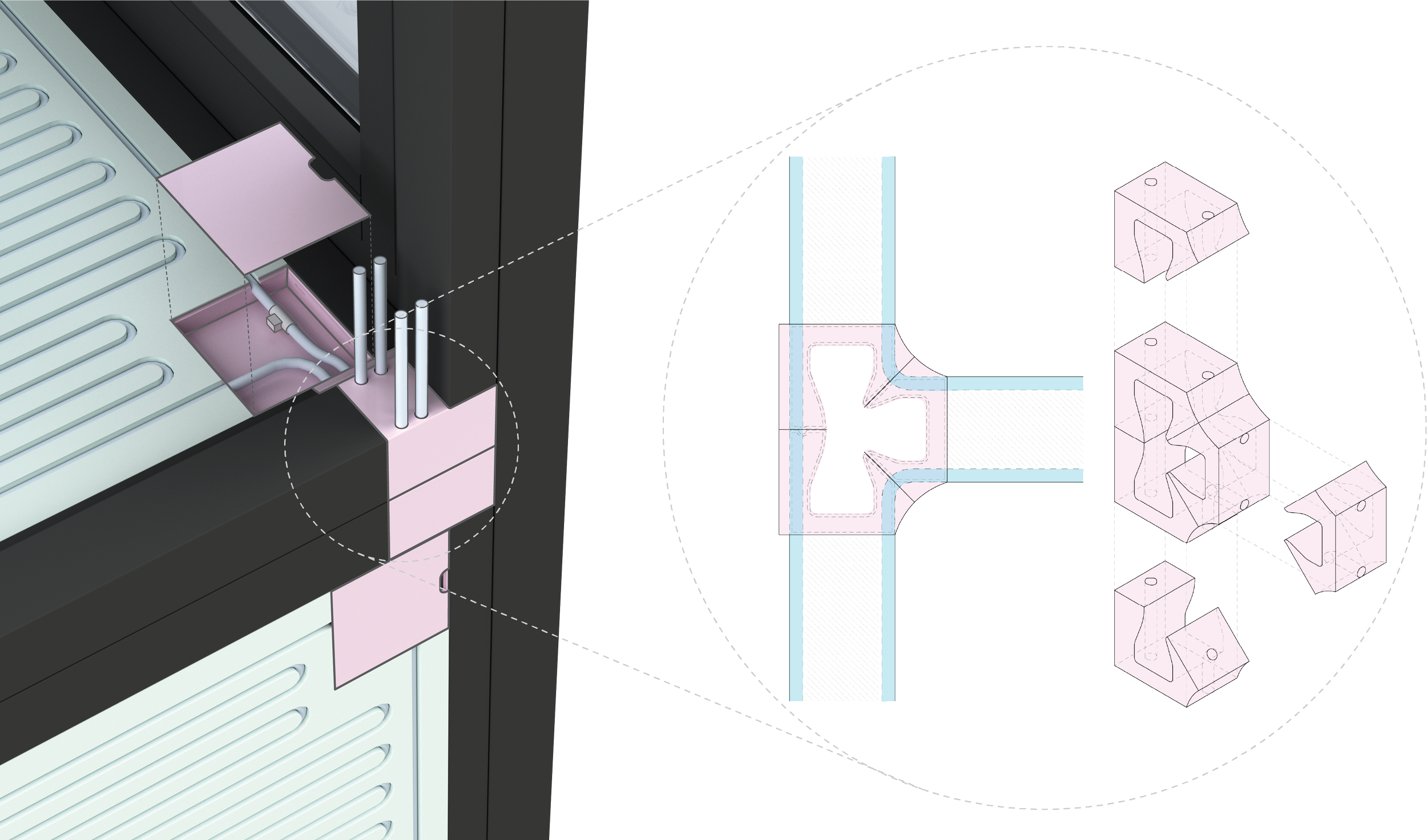
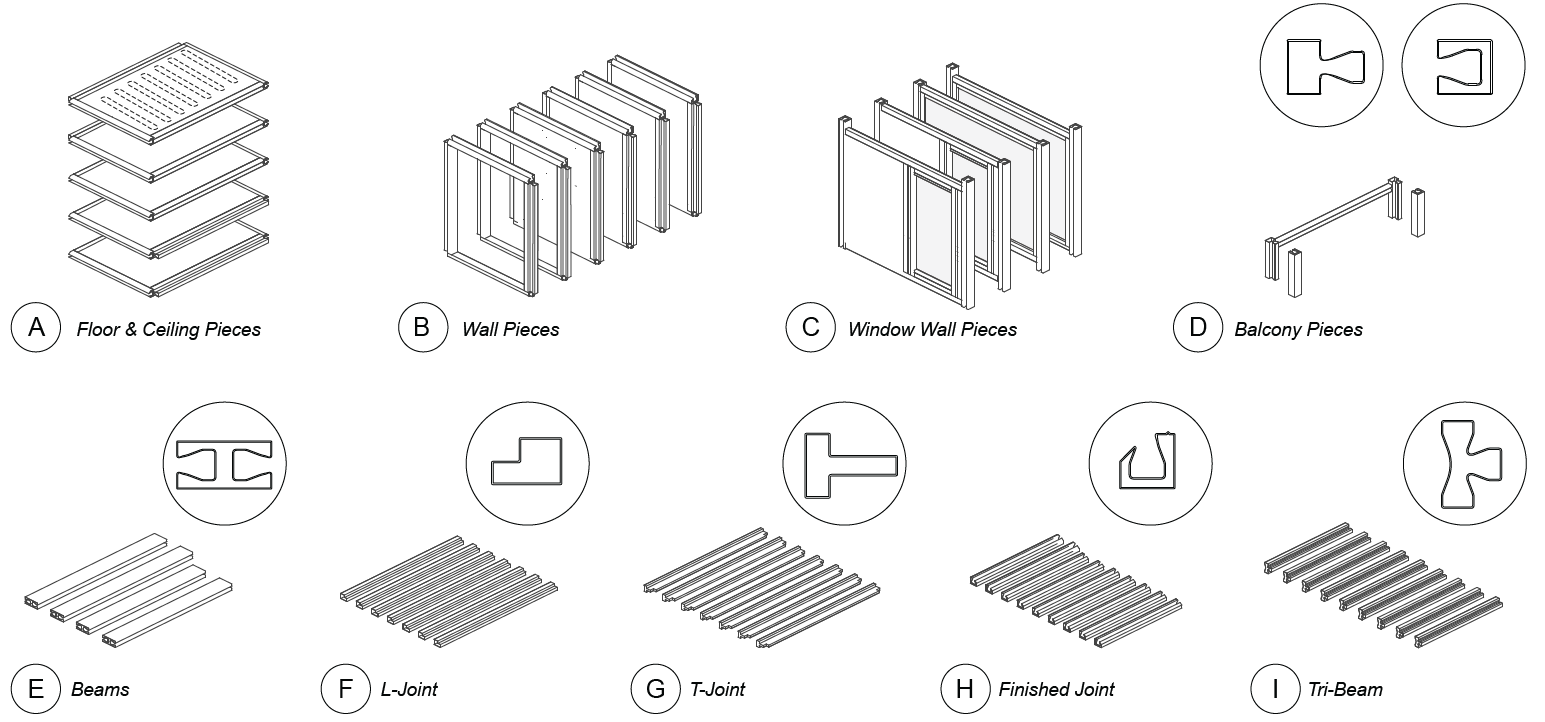
To ensure simplicity and repeatability in the fabrication process, a limited number of pulltruded joints have been developed that utilize a single male connector for multiple types of female connectors. These joints are strategically installed along the periphery of the SIP modules. By choosing appropriate profiles for assembly, the Plug-and-Play system is versatile enough to accommodate a wide range of building components, including the roof, slab, interior partitions, and even a window system.
To expand the applicability of the proposed modular construction system, a climate-adaptive hydronic system has been integrated. In essence, we are developing a modular construction system that simultaneously addresses the structural as well as energy aspects of envelope performance within one prefabricated system. By integrating the hydronic heating and cooling system, CASE expects that the proposed module can contribute to reducing both building energy use and carbon emissions.
Project Date: 2022-present
Researchers: Alexandros Tsamis, Youngjin Hwang, Gillian Strothenke, and Gabriela Toscano

